Network
A network consists of a collection of computers, printers
and other compatible equipment/ hardware that is connected together so that
they can communicate with each other.
Networking is a combination of two
words Connection & Packet. Before going further deep you need to understand
about these words.
Connection
A connection refers to physical connectivity (direct
or indirect) between Listener & Speaker (or Sender & Receiver).
Packet
The most basic unit that is transferred over a network.
When communicating over a network, packets are the envelopes that carry your
data (in pieces) from one end point to the other. It also uses in the
initiating process of networking before actually transferring the data, just
for checking the connectivity.
There are three types of Network Configuration:
 |
| Peer-to-Peer Network |
Peer –to- Peer Network
A
peer-to-peer (P2P) network is created when two or more PCs are connected and
share resources without strict security. All the peers connected through copper
wires.
The initial use of P2P networks in
business followed the deployment in the early 1980s of free-standing PCs.
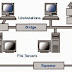
Client/Server Network
Client/server
networks are more suitable for larger networks. A central computer, or
'server', acts as the storage location for files and applications shared on the
network.
Client/server is a program
relationship in which one program (the client) requests a service or resource
from another program (the server). The server also controls the network access
of the other computers which are referred to as the 'client' computers.
All rights preserved by the Admin
only. Everything goes under the control of the Admin. In this type of structure
Monitoring & Security can easily be managed.
 |
| Client/ Server Network |
Thin Client Network
Thin client
usually refers to software, it is increasingly used for computers, such as
network computers and Net PCs, that are designed to serve as the clients for
client/server architectures. A thin client is a network computer without a hard
disk drive, whereas a fat client includes a disk drive.
There are three ways for Computer Network Designs is by their scope or scale:
LAN
A LAN (Local Area Network) is
a group of computers and network devices connected together, usually within the
same building.
The connections must be high speed
and relatively inexpensive.
LAN connection speeds can be
10Mbps or 100Mbps or 1000Mpbs also. LAN uses Guided Media
 |
| LAN |
WAN
A WAN (wide area network), in
comparison to a MAN, is not restricted to a geographical location, although it
might be confined within the bounds of a state or country. A WAN connects
several LANs, and may be limited to an enterprise (a corporation or an
organization) or accessible to the public. The technology is high speed and
relatively expensive. The Internet is an example of a worldwide public WAN.
WAN connection speeds can be
10Mbps or 100Mbps. WAN mainly uses Guided Media or Unguided media. Its long
distance communications, which may or may not be provided by public packet
network.
MAN
A MAN (metropolitan area
network) is a larger network that usually spans several buildings in the same
city or town.
A MAN is larger than a LAN, which
is typically limited to a single building or site. Depending on the
configuration, this type of network can cover an area from several miles to
tens of miles. A MAN is often used to connect several LANs together to form a
bigger network. When this type of network is specifically designed for a
college campus, it is sometimes referred to as a campus area network, or CAN.
MAN connection speeds can be
10Mbps or 100Mbps. MAN uses Guided Media or Unguided media.
There are three types of Network Configuration based on Uses:
Internet
It is a Global network
of computers, (servers or clients) to exchange information. It is a
"network of networks" that includes millions of private and public, academic, business, and
government networks (local or Global), linked by copper wires, wireless
connections, and other technologies.
Intranet
Internal company network
that uses Internet standards (HTML, HTTP & TCP/IP protocols) &
software.
An intranet is a private network
that is setup and controlled by an organization to encourage interaction among
its members, to improve efficiency and to share information, among other
things.
An intranet is a restricted-access
network that works much like the Internet, but is isolated from it. As is the
case with the Internet, an intranet is based on TCP/IP protocols.
Extranet
An extranet is an
extended intranet. In addition to allowing access to members of an
organization, an extranet uses firewalls, access profiles, and privacy
protocols to allow access to users from outside the organization. In essence,
an extranet is a private network that uses Internet protocols and public
networks to securely share resources with customers, suppliers, vendors,
partners, or other businesses.
Both intranets and extranets are
owned, operated and controlled by one organization. However, the difference
between intranets and extranets is defined in terms of who has access to the
private network and the geographical reach of that network. Intranets allow
only members of the organization to access the network, while an extranet
allows persons from outside the organization (i.e. business partners and
customers) to access the network.
 |
| Difference b/w Internet, Intranet & Extranet |
------







This information is impressive; I am inspired with your post writing style & how continuously you describe this topic. After reading your post, thanks for taking the time to discuss this, I feel happy about it and I love learning more about this topic.
ReplyDeleteRegards,
ccna course in Chennai|ccna training in Chennai|ccna institutes in Chennai