Here is good news for you, if you have an old PC hardware. Don’t
throw it away. It can eliminate the need of purchasing a router for your small
network.
A Linux system could work as a powerful router in small network. You
only have to install a Linux Distro on your PC/Laptop and install an extra NIC
if you only have one. It only takes two minutes to configure a Linux machine as
a router. This blog show you how to configure Linux as a router in few simple
steps.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system with two or more interfaces.
- Internet Connection.
- IP tables basic knowledge(need not to be a geek).
- Another system on LAN for testing.
- Dnsmasq (if a DHCP is not working in your LAN environment).
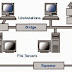
Topology
Steps
- Configuring ip address
edit network connection setting from the setting menu
 |
| Config IP Address |
- Enable ip forwarding
Run this command in terminal
sudo echo 1 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
This will give output as
1 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
To make the change permanent so after next boot you don't have to
enable ip forwarding again. Edit
/etc/systcl.conf
and uncomment the line
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
- For enabling NATing issue the command:
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j
MASQUERADE
- Configuring firewall to allow inbound and outbound transit traffic by the follwoing commands:
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth1 -o eth0 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o eth1 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
- Configuring dnsmasq
Dnsmasq is a lightweight dns cum dhcp/tftp server and it is easily
configurable. Just uncomment the line:
#dhcp-range=192.168.0.50,192.168.0.150,12h
Here u can change the range with your choice of subnet, no need to change other things dnsmasq will automatically provide default router and DNS server ip address as the ip of machine it is running on.
(NOTE: if you have a DHCP serer already in your environment you
need not to follow this step just configure your DHCP to provide gateway ip
address as the ip address of LAN facing interface of Linux machine or set
"option 3 " as the ip address of Linux machine.)
- Test the connectivity to internet on test pc
(NOTE: The interface used here i.e. eth0 & eth1 could be
different on your machine i.e. the machine can be connected to internet via a
PPP (point to point) or wireless connection, so make change in configuration
according to your need.)









Good explanation, thanks
ReplyDeleteIf you run §sudo echo 1 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward§ nothing happens, it just prints §1 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward§ as §root§, which is completely pointless.
ReplyDelete